JAVA 速学笔记4
Contents
ArrayList
- 集合的概念:
- 集合是一个容器,是一个载体,一次可以容纳多个对象
- 相比之前的数组,数组必须规定大小,集合可以不确定
- 集合储存的是什么?
- 集合不能直接存储基本的数据类型
- 集合也不能直接存储对象
- 集合中储存的是对象在内存中的地址(或者叫做引用)
- 集合本身也是一个对象
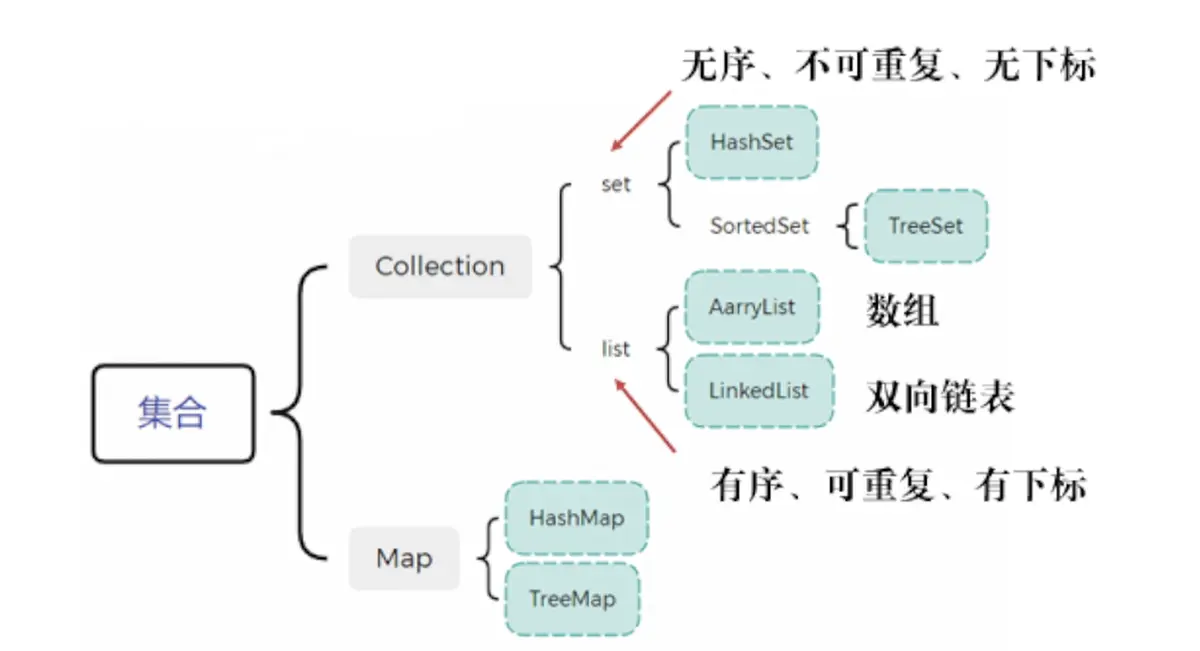
- 集合的数据结构:
- 不同的集合,底层对应不同的数据结构。向不同的集合中存储数据,等于向不同的数据结构存储数据。
- 数据结构:数据的存储方式。(数组、链表、树、哈希表、图等)
- Collection:以单个元素形式储存
- Map:以键值对形式储存
1 | public class Sutdent { |
1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
异常处理
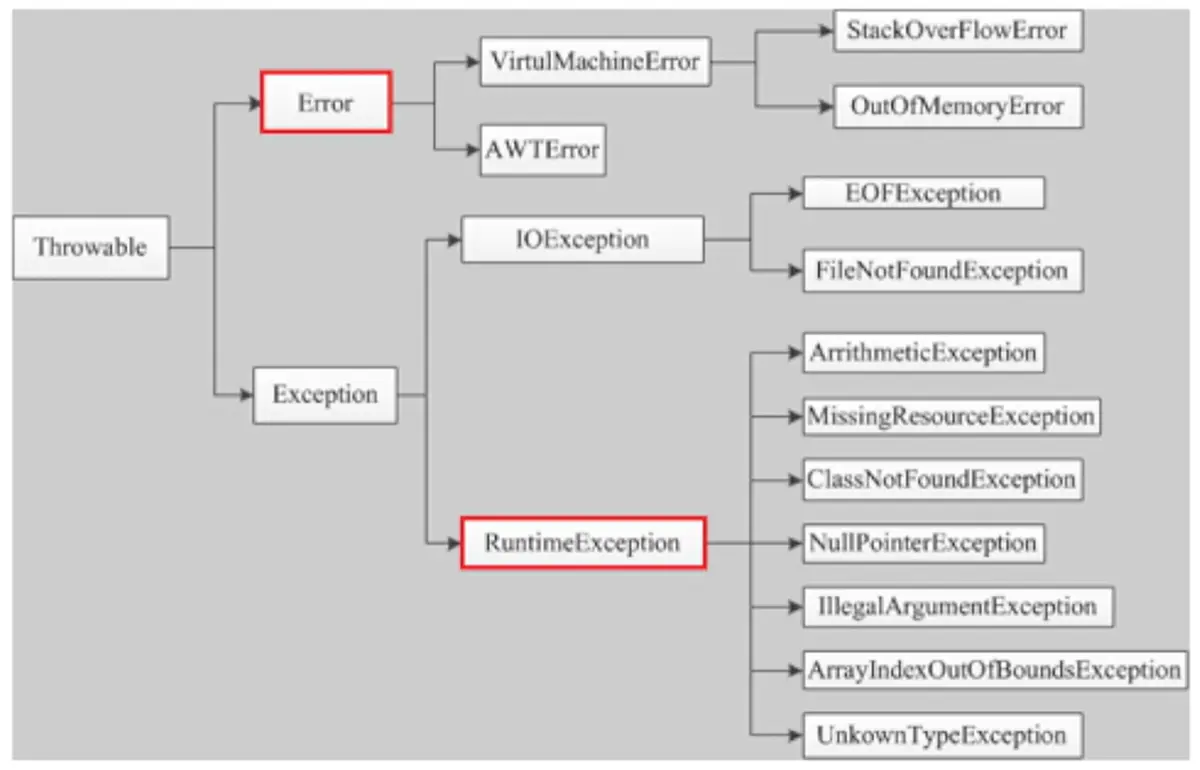
错误上抛处理
1 | import java.util.Scanner; |
错误自己处理
1 | import java.util.Scanner; |